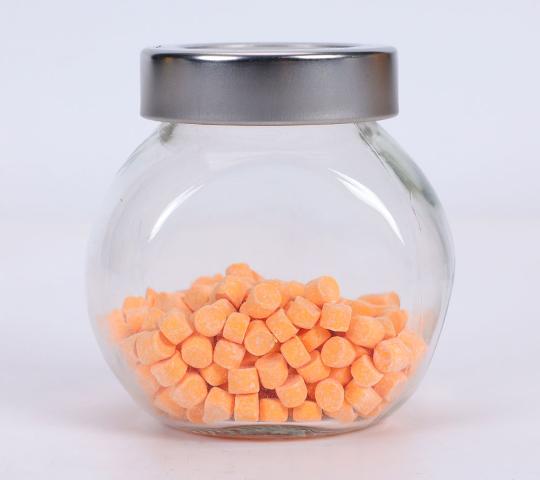
The ability to create lightweight, durable, and visually appealing products often comes down to one secret ingredient — the AC blowing agent, scientifically known as Azodicarbonamide. This high-performance additive has quietly powered industries ranging from sports equipment to building materials, giving products the kind of smooth texture, uniform cell structure, and dependable strength that customers expect.
Let’s explore what makes AC blowing agents so essential.
Basic Information of AC Blowing Agent
Chemical Structure and Molecular Formula
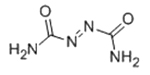
The AC blowing agent, or Azodicarbonamide, has the molecular formula C₂H₄N₄O₂ and a molecular weight of 116.08 g/mol.
It belongs to the azo compound family, characterized by nitrogen–nitrogen double bonds, which play a key role in its foaming ability. Its CAS number is 123-77-3.
Physical Properties
- Appearance: Orange powder
- Particle Size: 8–10 μm (fine and uniform for even distribution)
- Purity: ≥98%
- Residue on 38 μm sieve: ≤0.1%
- Decomposition Temperature: ≥200°C
These properties make it easy to incorporate into polymer and rubber compounds without affecting product color or causing mold corrosion.
Chemical Properties
Thermal Decomposition
Upon heating to its decomposition temperature (around 200°C), AC foaming agent releases gases such as nitrogen, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and ammonia. These gases form a fine, closed-cell foam structure within the polymer matrix.
Thermal Stability
The high decomposition temperature provides excellent thermal stability during processing. This stability ensures that premature foaming does not occur, which is critical for achieving consistent cell structures.
Compatibility
AC foaming agents are compatible with a wide variety of thermoplastics and elastomers, including PVC, PE, PS, EVA, PP, ABS, polyamide, and natural or synthetic rubber. This versatility allows manufacturers to use a single foaming agent across multiple product lines.
Working Principles

The magic of AC blowing agents lies in controlled gas release. When incorporated into a plastic or rubber compound and heated during processing, the agent decomposes, releasing gas bubbles throughout the material. These bubbles remain trapped, creating a foamed structure. This process reduces material density, improves thermal and sound insulation, and can enhance cushioning properties without compromising structural integrity.
Applications
Plastic
In plastics like PVC, PE, PS, EVA, and ABS, AC foaming agents help create lightweight sheets, profiles, and molded parts. They are used in packaging materials, insulation boards, and consumer products where reduced weight translates into lower transportation costs and easier handling.
Rubber
In rubber applications, such as shoe soles, sports mats, and sealing gaskets, AC blowing agents deliver uniform cell structures and smooth surfaces. The foam maintains flexibility, comfort, and durability — qualities essential for high-performance athletic gear and automotive components.
Construction
In the construction sector, AC blowing agents are used in insulation materials, foam panels, and sealing strips. They improve thermal efficiency, soundproofing, and weight-to-strength ratios, making building materials easier to install and more energy-efficient.
From footwear to construction panels, AC blowing agents are the invisible architects behind lighter, stronger, and more efficient products. With stable performance, wide compatibility, and proven reliability, they remain a go-to solution for manufacturers looking to improve both product quality and production efficiency. Whether used under normal or high pressure, this versatile additive continues to play a quiet yet powerful role in shaping modern materials.
 vaskokudrickrk136@gmail.com
vaskokudrickrk136@gmail.com Jiaxing Beihua Polymer Auxiliaries Co., Ltd. / Shanghai Crystal Wells Chemical New Materials Co., Ltd.
Jiaxing Beihua Polymer Auxiliaries Co., Ltd. / Shanghai Crystal Wells Chemical New Materials Co., Ltd.

































